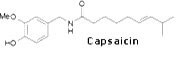
Therapeutic constituents:
Principal Constituents, The pungent principle Capsaicin was identified from the fruits1.
Capsicoside A is also identified from the fruits2. Chilli contains capsaicin, carotenoids, flavonoids, volatile oil and steroidal saponins. Capsaicin stimulates blood circulation. It topically desensitizes nerve endings and acts as a local analgesic (Indian Medicinal Plants—An Illustrated Dictionary, C.P.Khare. 129. 2007). Chilies are an excellent source of vitamins A, B, C and E and folic acid.
Pharmacology
Capsaicin (50mg/Kg, s.c.) treatment of 2-day old female rats resulted 3 months later in 81.0% decrease in mean pain response to tail-vein injection of HCl and 63.0 and 72.0 % increase in nociceptive threshold in rats with normal and inflamed paws respectively 3.
Toxicology
It is irritant to skin but the administration of capsaicin in sub-cutaneous or intraperitoneal administration into guinea pigs and rats makes them tolerant to various irritants including capsaicin4.
Key therapeutic benefits:
In the form of ointment of plasters, it is used externally for the treatment of rheumatism, lumbago, and neuralgia. Capsicum wool, prepared by dissolving the oleoresin in ether and pouring it on absorbent cotton wool, is useful in rheumatoid affections. Chilli, in small doses, is a powerful stimulant and carminative. Chilies are detoxifiers which help the body get rid of accumulated toxins.The presence of folic acid and vitamin B in Chillies reduces the risk of heart disease.
Externally applied, the herb alleviates joint pain as a result of rheumatoid arthritis
Used in Movido
References
- Abst., 1973, 79, 123698.
- Harborne, J.B., 1999, Phytochemical Dictionary, Taylor and Francis Ltd., London.
- Pharm.Pharmacol. 1980, 32, 656.
- Mathew al., Flavour Ind, 1971, 2, 691 & Monsereenusorn, Quart J Crude Drug Res, 1980, 18, 1.